Static vs. Dynamic Mixing Equipment: Which Is Right for Your Process?
In industrial processing, selecting the appropriate mixing equipment is crucial for product quality, operational efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. Two primary categories of mixers—static and dynamic—serve diverse applications across industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and adhesives. Understanding the distinctions between these mixing technologies is essential for optimizing your process.
Understanding Static Mixing Equipment
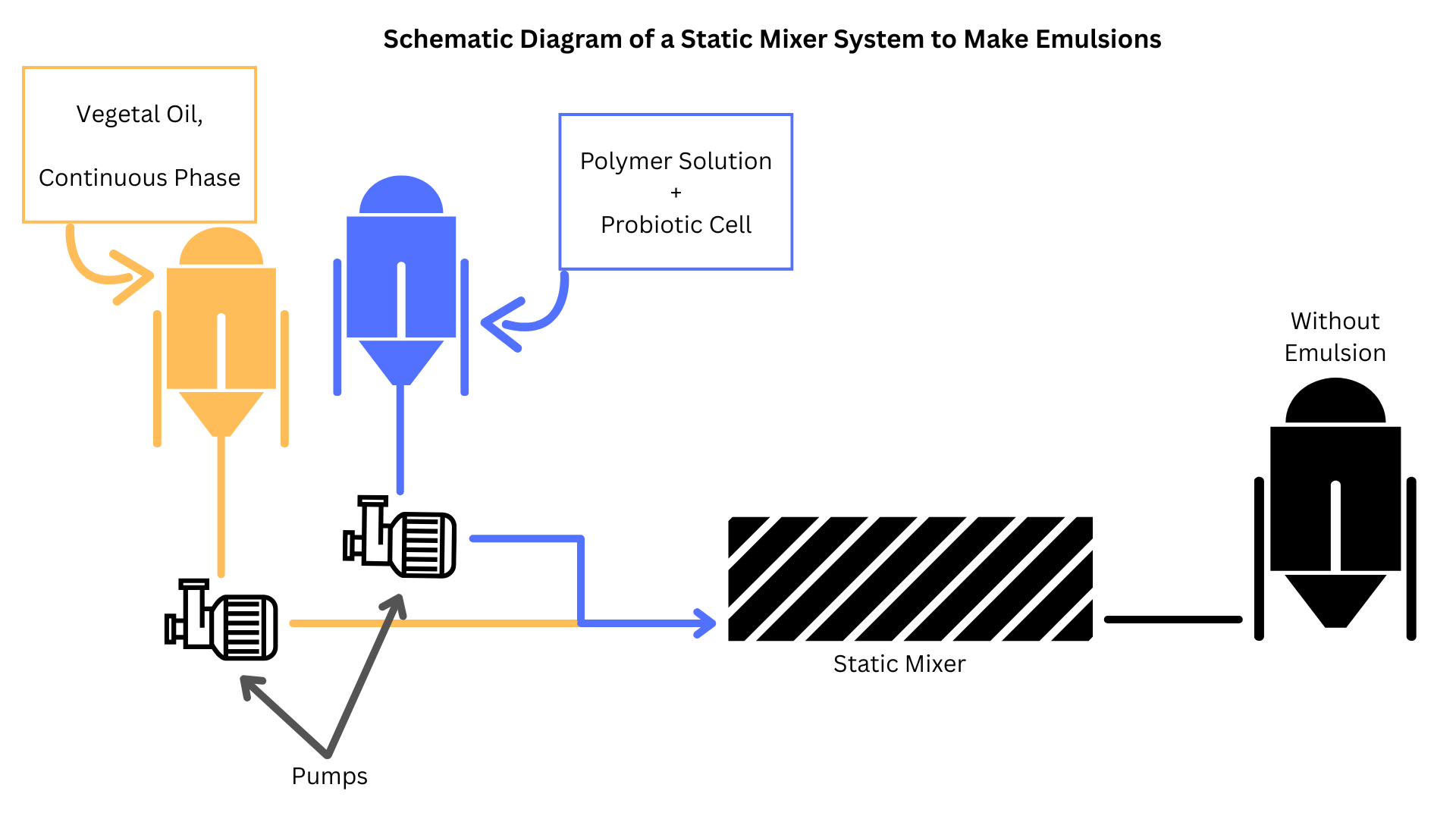
Static mixers, also known as motionless mixers, are devices installed within pipelines to mix fluids as they flow through. They contain stationary elements—such as baffles or blades—arranged to create turbulence and promote mixing without moving parts or external power sources. As fluids pass through, they are divided and recombined multiple times, resulting in a homogeneous mixture.
Key advantages of static mixers include:
- Energy Efficiency: No moving parts means lower energy consumption.
- Low Maintenance: Minimal wear and tear reduce maintenance requirements.
- Compact Design: Easily integrated into existing piping systems.
Static mixers are ideal for continuous processes involving low- to medium-viscosity fluids, such as blending chemicals, diluting acids, or mixing gases.
Exploring Dynamic Mixing Equipment
Dynamic mixers, or mechanical mixers, utilize rotating components—such as impellers or blades—to actively mix fluids. These mixers are powered by motors and can be configured for batch or continuous processing. They offer precise control over mixing intensity and are suitable for a wide range of viscosities and complex mixing tasks.
Benefits of dynamic mixers include:
- Versatility: Capable of handling various fluid types and viscosities.
- Enhanced Mixing: Effective for emulsifying, dispersing solids, and achieving uniform mixtures.
- Adjustable Parameters: Mixing speed and intensity can be tailored to specific process requirements.
Dynamic mixers are commonly used in applications requiring thorough mixing, such as producing creams, suspensions, or high-viscosity adhesives.
Comparing Static and Dynamic Mixers
Feature
Energy Consumption
Maintenance
Installation
Mixing Efficiency
Cost
Static Mixers
Low (no external power needed)
Minimal (no moving parts)
Simple (inline integration)
Effective for low to medium viscosity fluids
Lower initial and operating costs
Dynamic Mixers
Higher (requires motorized components)
Regular (due to mechanical wear)
More complex (requires space for motor and controls)
Suitable for a wide range of viscosities
Higher initial investment and operating costs
The choice between static and dynamic mixers depends on factors such as fluid properties, desired mixing quality, process scale, and budget constraints.
Application Scenarios
Static Mixer Example: In a water treatment facility, a static mixer is used to blend chlorine into the water stream. The mixer’s design ensures thorough mixing without the need for external power, leading to energy savings and reduced maintenance.
Dynamic Mixer Example: A pharmaceutical company employs a dynamic mixer to produce a high-viscosity cough syrup. The mixer’s adjustable speed and shear capabilities ensure a uniform product, critical for dosage consistency.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Mixing Equipment
- Fluid Characteristics: Viscosity, density, and chemical properties influence mixer selection.
- Process Requirements: Continuous vs. batch processing, mixing time, and desired homogeneity levels.
- Space and Infrastructure: Available space and existing system compatibility.
- Cost Considerations: Initial investment, operating costs, and maintenance expenses.
- Regulatory Compliance: Industry-specific standards and cleanliness requirements.
Conclusion
Selecting the appropriate mixing equipment is vital for process efficiency, product quality, and cost management. Static mixers offer simplicity and energy savings for suitable applications, while dynamic mixers provide versatility and control for more complex mixing tasks.
For further insights into mixing technologies and their applications, consider exploring the following resources:
- Static Mixers Vs Dynamic Mixers: Which Is Right For Your Process?
- Dynamic Mixing Vs. Static Mixing - Dispensing.com
If you have questions or need assistance in selecting the right mixing equipment for your process, feel free to reach out to our team for expert guidance.