What Is Glass‑Lined Mixing Equipment? A Beginner’s Guide
Glass-lined mixing equipment—including reactors, tanks, and agitators—combines chemical resistance with mechanical reliability. In this beginner’s guide, we examine how glass-lined systems work, why they are essential in corrosive environments, and how to use and maintain them for optimal performance.
Understanding Glass-Lined Mixing Equipment
Glass-lined mixing equipment consists of vessels—typically steel tanks or reactors—coated internally with a layer of borosilicate glass. This glass welds seamlessly to the steel shell at high temperatures during manufacturing, creating a composite container that offers the strength of steel and the inertness of glass. Operators use these vessels with agitators, baffles, and nozzles to mix or react corrosive chemicals. From small lab reactors to 10,000 L production tanks, glass-lined systems come in various sizes and configurations.
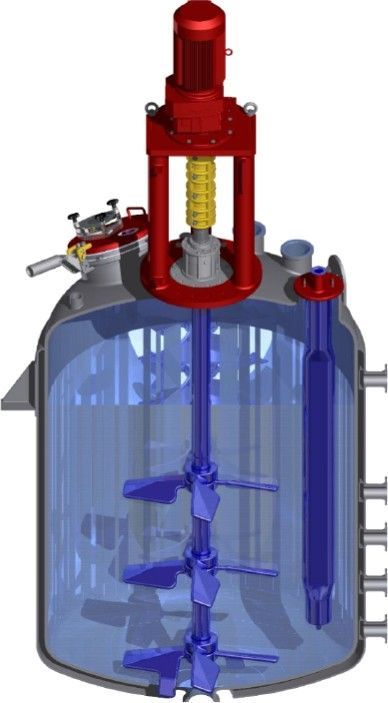
Why Use Glass-Lined Equipment?
Chemical Resistance and Purity
Glass-lined vessels are uniquely resistant to strong acids, alkalis, and solvents while preventing metal contamination—key for high-purity chemical, pharmaceutical, and food processes. The glass lining creates an inert barrier that helps maintain product integrity and extend equipment life.
Thermal and Abrasion Resistance
Glass-lined systems withstand sudden temperature changes (thermal shock) better than stainless steel, making them suitable for heating and cooling cycles. The hard glass lining also resists abrasion and mechanical wear, preserving performance over the long term.
Types of Glass-Lined Vessels and Mixers
Stirred Reactors and Tanks
These vessels include internal components like baffles, impellers, and jackets—designed for batch reactions or mixing, often with agitators machined to glass, steel, or both. Agitators are typically housed in sealed shafts to prevent glass breakage.
Static Mixers
Glass-lined static mixers are inline baffle plates installed in pipes to achieve continuous blending without moving parts, ideal for corrosive media and gas-liquid mixing.
Agitation Systems
Innovative glass-lined agitators, such as Pfaudler’s multi-stage 7-turbine units, offer improved mixing efficiency and wear resistance in harsh process conditions.
Key Benefits of Glass-Lined Equipment
- Corrosion Protection—Glass prevents corrosive chemicals from damaging steel.
- Product Purity—Smooth glass surfaces reduce contamination and cross-reactivity.
- Ease of Cleaning—Glass-lined tanks are compatible with CIP/SIP methods thanks to non-stick, sanitary interiors.
- Visual Monitoring—Some systems feature translucent glass linings or sight glasses for reaction observation.
- Durability—The glass-steel composite resists impact, heat, and corrosion for decades
Applications Across Food and Beverage Products
Mixing equipment finds applications across a broad spectrum of products:
- Dairy: Homogenizing milk and yogurt to prevent cream separation.
- Beverages: Blending juices, soft drinks, and alcoholic beverages for consistent flavor.
- Confectionery: Mixing ingredients for candies and chocolates to achieve desired textures.
- Bakery: Combining dough and batters uniformly for consistent baking results.
- Sauces and Dressings: Emulsifying oil and water phases to create stable products.
Each application demands specific mixing parameters to ensure product quality and safety.
Typical Applications
Glass-lined mixing equipment serves a variety of industrial uses:
- Acid/Alkali Reactions, Polymerization, Coatings
- Pharmaceutical API Manufacturing—Purity-critical production
- Food & Beverage—Acidic flavoring or enzymatic processes
- Specialty Chemicals & Petrochemicals—Chlorination, nitrification, solvent blends
- Water Treatment and Recycling—Handling corrosive wastes or cleaning solutions
Design & Manufacturing Essentials
Creating a glass-lined mixer requires precise processes:
- Glass Application and Firing: Glass frit is applied to steel and fired at circa 900°C to form a crystalline bond.
- Layer Specs: Linings typically range from 1–3 mm in thickness, sometimes in multiple layers for durability.
- Component Integration: Glass-lined agitators, baffles, sight panels, and jackets are built into the vessel design.
- Quality Standards: Conformity with standards like DIN 28136 ensures interchangeability and reliable performance.
Operating Best Practices
- Prevent Thermal/Shock Limits: Avoid rapid >110°C temperature swings to prevent liner damage.
- Approved Cleaners Only: Use non-abrasive detergents, soft brushes, and CIP tools to preserve glass integrity.
- Periodic Inspections: Conduct spark testing and visual checks to detect micro-cracks early.
- Handle With Care: Minimize mechanical impact on mixing parts and implement safe loading procedures.
Limitations and Considerations
- Not Universal: Glass lining is unsuitable for hydrofluoric acid or phosphorus over 30% at high temperatures.
- Gentle Handling Needed: Avoid mechanical shocks to maintain liner lifespan.
- Higher Initial Cost: Although the upfront cost is higher, long-term reliability usually offsets it.
- Design Constraints: For extreme pressures or viscosities, alternative alloys may be more suitable.
Enhancing Performance with Glass-Lined Systems
Manufacturers combine glass-lined vessels with optimized agitation systems for better performance.
- Custom Agitators & Baffles: Adjustable blade systems (e.g., GlasLock) improve dynamic mixing efficiency.
- Mixing Simulations: CFD technology helps match impeller designs to process needs.
- Retrofitting Flexibility: Glass-lined agitators like Pfaudler ProSol retrofit into existing vessels for process upgrades.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can glass liners be repaired on-site?
Yes—specialist teams reline vessels or apply repair patches using similar glass frit.
How long do they last?
With proper care, vessels can last 20–30 years due to corrosion resistance.
Can I monitor reactions visually?
Glass tops and sight glasses allow visual monitoring for safety and quality control.
Conclusion
Glass-lined mixing equipment plays a critical role in handling corrosive chemicals while ensuring process purity and reliability. From design and fabrication to application, cleaning, and troubleshooting, this beginner’s guide provides a foundation for using these specialized systems effectively. For help choosing, installing, or maintaining glass-lined equipment, reach out—our experts are ready to support your needs.

